International standard for medical imaging and related information exchange
DICOM - Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine
DICOM (Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine) is the international standard for medical images and related information. It defines the formats for medical images that can be exchanged with the data and quality necessary for clinical use.
Educational Purpose Notice: This content is provided for educational and reference purposes only. For actual DICOM implementation in medical imaging systems, always consult the official DICOM standard documentation and work with certified DICOM specialists.
What is DICOM?
DICOM enables the integration of medical imaging devices including scanners, servers, workstations, printers, network hardware, and picture archiving and communication systems (PACS) from multiple manufacturers.
The standard addresses:
- Image Format: How medical images are stored and structured
- Network Communication: How imaging devices communicate
- Media Storage: How images are stored on removable media
- Print Management: How images are printed
- Query/Retrieve: How to search for and retrieve images
DICOM Architecture
DICOM architecture showing the layered structure from application services down to network transport
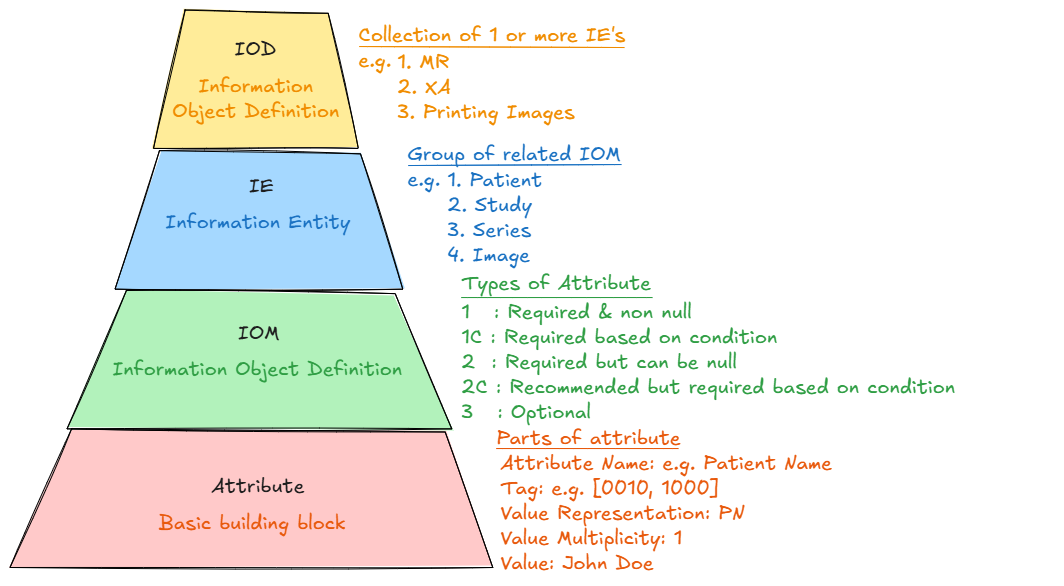
Information Object Definitions (IODs)
DICOM defines various types of medical information as Information Objects:
- CT Image: Computed Tomography scans
- MR Image: Magnetic Resonance images
- US Image: Ultrasound images
- X-Ray Image: Radiographic images
- RT Structure Set: Radiation therapy structures
- Patient: Patient demographic information
- Study: Collection of imaging procedures
- Series: Group of related images
Service Classes
DICOM defines services for different operations:
- Storage: Storing medical images and data
- Query/Retrieve: Finding and retrieving images
- Print Management: Printing medical images
- Modality Worklist: Managing imaging procedures
- Structured Reporting: Creating structured reports
DICOM Data Structure
DICOM File Format
A DICOM file contains both the medical image and metadata in a structured format:
DICOM File Structure:
├── File Preamble (128 bytes)
├── DICOM Prefix ("DICM")
├── File Meta Information
└── Data Set
├── Patient Information
├── Study Information
├── Series Information
├── Image Information
└── Pixel Data
DICOM file structure showing hierarchical organization of medical imaging data
DICOM Tags
DICOM uses tags to identify different data elements:
Common DICOM Tags:
(0010,0010) Patient's Name
(0010,0020) Patient ID
(0010,0030) Patient's Birth Date
(0010,0040) Patient's Sex
(0020,000D) Study Instance UID
(0020,000E) Series Instance UID
(0008,0018) SOP Instance UID
(0028,0010) Rows
(0028,0011) Columns
(7FE0,0010) Pixel Data
Example DICOM tags for patient demographics and image properties
Value Representations (VR)
DICOM defines how different types of data are encoded:
- AE: Application Entity (16 bytes max)
- AS: Age String (4 bytes fixed)
- CS: Code String (16 bytes max)
- DA: Date (8 bytes fixed, YYYYMMDD)
- DS: Decimal String (16 bytes max)
- DT: Date Time (26 bytes max)
- IS: Integer String (12 bytes max)
- LO: Long String (64 chars max)
- PN: Person Name (64 chars max per component)
- SH: Short String (16 chars max)
- TM: Time (16 bytes max, HHMMSS.FFFFFF)
- UI: Unique Identifier (64 bytes max)
DICOM Network Services
DICOM Upper Layer Protocol
DICOM uses a specialized network protocol for communication between devices:
DICOM Network Communication:
Client (SCU) ←→ Server (SCP)
│ │
├─ Association Request
│ │
│ ←─ Association Accept
│ │
├─ DICOM Commands/Data
│ │
│ ←─ DICOM Responses
│ │
├─ Release Request
│ │
│ ←─ Release Response
DICOM network communication flow between Service Class User (SCU) and Service Class Provider (SCP)
DIMSE | C-STORE (Storage)
Stores DICOM objects on a remote system:
# Example DICOM C-STORE operation (pseudocode)
def store_dicom_image(image_path, destination_ae):
# Create association with destination
assoc = create_association(destination_ae)
# Read DICOM file
dataset = read_dicom_file(image_path)
# Send C-STORE request
response = assoc.send_c_store(dataset)
# Handle response
if response.Status == 0x0000:
print("Storage successful")
else:
print(f"Storage failed: {response.Status}")
# Release association
assoc.release()
Example DICOM C-STORE operation for storing medical images
DIMSE | C-FIND (Query)
Searches for DICOM objects based on specified criteria:
# Example DICOM C-FIND operation (pseudocode)
def find_patient_studies(patient_id, query_ae):
# Create query dataset
query = Dataset()
query.QueryRetrieveLevel = 'STUDY'
query.PatientID = patient_id
query.StudyDate = '' # Return all dates
query.StudyDescription = ''
query.StudyInstanceUID = ''
# Perform C-FIND
responses = query_ae.send_c_find(query)
for response in responses:
if response.Status == 0xFF00: # Pending
print(f"Study: {response.StudyDescription}")
print(f"Date: {response.StudyDate}")
print(f"UID: {response.StudyInstanceUID}")
Example DICOM C-FIND operation for querying patient studies
DIMSE | C-MOVE (Retrieve)
Retrieves DICOM objects from a remote system:
# Example DICOM C-MOVE operation (pseudocode)
def retrieve_study(study_uid, source_ae, destination_ae):
# Create retrieve dataset
retrieve = Dataset()
retrieve.QueryRetrieveLevel = 'STUDY'
retrieve.StudyInstanceUID = study_uid
# Perform C-MOVE
responses = source_ae.send_c_move(retrieve, destination_ae)
for response in responses:
if response.Status == 0xFF00: # Pending
print(f"Moving {response.NumberOfRemainingSuboperations} objects")
elif response.Status == 0x0000: # Success
print("Move completed successfully")
Example DICOM C-MOVE operation for retrieving medical images
DICOM Implementation Considerations
Security and Privacy
- Patient Privacy: Ensure PHI protection and HIPAA compliance
- Network Security: Use secure communication protocols
- Access Control: Implement proper authentication and authorization
- Audit Logging: Maintain comprehensive audit trails
- Data Integrity: Verify image integrity and authenticity
Performance Optimization
- Compression: Use appropriate image compression (JPEG, JPEG 2000)
- Network Optimization: Optimize for bandwidth and latency
- Storage Management: Implement efficient storage strategies
- Caching: Use intelligent caching for frequently accessed images
Interoperability
- Conformance Statements: Document DICOM capabilities
- IHE Profiles: Follow Integrating the Healthcare Enterprise profiles
- Testing: Perform thorough interoperability testing
- Validation: Validate DICOM conformance
DICOM Tools and Libraries
Open Source Libraries
- DCMTK: Comprehensive DICOM toolkit (C++)
- pydicom: Python library for DICOM file handling
- fo-dicom: .NET DICOM library
- dcm4che: Java DICOM toolkit
- GDCM: Grassroots DICOM library
Commercial Solutions
- Merge DICOM Toolkit: Enterprise DICOM development
- LEADTOOLS Medical: Comprehensive medical imaging SDK
- Accusoft DICOM: DICOM viewing and processing
Learning DICOM
For healthcare IT professionals and developers:
- Understand Medical Imaging: Learn basic radiology concepts
- Study DICOM Standard: Read the official DICOM specification
- Practice with Tools: Use DICOM viewers and editors
- Implement Basic Operations: Start with C-STORE and C-FIND
- Join DICOM Community: Participate in DICOM working groups
Official DICOM Resources
For implementation and detailed specifications, always consult official DICOM documentation:
- DICOM Standard: https://www.dicomstandard.org/
- DICOM Library: https://www.dicomlibrary.com/
- NEMA DICOM: https://www.nema.org/Standards/Pages/Digital-Imaging-and-Communications-in-Medicine.aspx
- IHE Radiology: https://www.ihe.net/ihe_domains/radiology/
- DICOM Conformance: https://www.dclunie.com/dicom-status/status.html
Important Note: This educational content provides an overview of DICOM concepts and implementation approaches. For production medical imaging systems, always refer to the official DICOM standard at https://www.dicomstandard.org/ and work with certified DICOM specialists to ensure compliance with medical device regulations and healthcare standards.
Tags
Implementation Reminder
This content is for educational purposes only. For production medical imaging systems, always refer to the official DICOM standard at https://www.dicomstandard.org/ and work with certified DICOM specialists to ensure compliance with medical device regulations and healthcare standards.